WHO WROTE FIRST SAMUEL?
Together, 1 and 2 Samuel form one book in the Hebrew Bible. The Greek translation of the Bible, the Septuagint, was the first version to divide the material into two parts. Though named after its main character, the prophet Samuel, the book does not claim an author. However, Samuel may have written, and he certainly supplied, the information for 1 Samuel 1:1–24:22, which is a biography of his life and career up to his death. First Chronicles 29:29 notes that Samuel, along with Nathan and Gad, recorded the “acts of King David.” Evidence in the writing suggests that the books of 1 and 2 Samuel were compiled by someone from the prophetic school who used documents from Samuel, Nathan, and Gad.1
WHERE ARE WE?
First Samuel 27:6 refers to the divided monarchy, when the 10 tribes of Israel rebelled against the two tribes of Judah, which occurred after Solomon’s reign. From this we can conclude that the book came together sometime after the death of David (971 BC) and perhaps even after the death of Solomon (931 BC). Because the book contains no reference to the Assyrian invasion in 722 BC, it likely originated before the period of the exile.
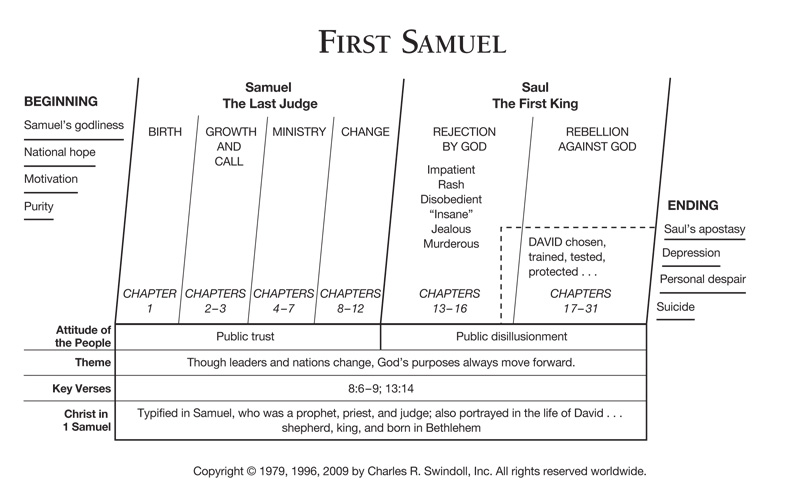
The events that happen in 1 Samuel took place over a period of about 110 years, stretching from the closing days of the judges, when Samuel was born (ca. 1120 BC) through the death of Saul (1011 BC). We see the birth of Samuel, his call from God and subsequent prophetic ministry, the rise and fall of King Saul, and the anointing and maturity of young David.
First Samuel is set in the land of Israel, where the Hebrews invaded and settled (see Joshua). Numerous other peoples continued to dwell alongside Israel, often disrupting the peace and encouraging the Israelites to stray from their faith.
WHY IS FIRST SAMUEL SO IMPORTANT?
In this critical period of Israel’s history, the people of God transformed from a loosely affiliated group of tribes into a unified nation under a form of government headed by a king. They traded the turmoil of life under the judges for the stability of a strong central monarchy.
First Samuel focuses on the establishment of that monarchy. The people demanded a king, similar to the kings of the surrounding nations (1 Samuel 8:5). Saul, the first king, though “head and shoulders above the rest” did not have a righteous heart, and his line was destined never to inherit the crown (9:1–15:35). God instructed Samuel to anoint David, the youngest son of Jesse of Bethlehem, as the next king (16:1–13).
Much of 1 Samuel follows David’s exploits as a young musician, shepherd, and warrior. We witness his underdog victory over Goliath (17:1–58), his deep friendship with Jonathan (18:1–4), and his growing military prowess (18:5–30). He waited patiently for the throne, often pursued and driven into hiding by Saul. The book concludes with Saul’s death (31:1–13), which serves as a natural dividing marker between 1 Samuel and 2 Samuel.
WHAT'S THE BIG IDEA IN 1 SAMUEL?
First Samuel chronicles the beginning of Israel’s monarchy, following the lives of the prophet Samuel, the ill-fated King Saul, and God’s ultimate choice of David as king. Several themes feature prominently.
Providence: God repeatedly made everyday events work for His purposes. He used Hannah’s contentious relationship with Peninnah (1 Samuel 1:1–28), led Saul to Samuel during Saul’s search for lost donkeys (9:1–27), and caused David to learn of Goliath while taking food to his brothers (17:1–58). These are but a few examples.
Kingship: As the divine King, God designated a human vice-regent, David, to rule over His people. This history validates David’s house as the legitimate rulers of Israel. It also fulfils Jacob’s promise that the sceptre will never depart from Judah, David’s tribe (Genesis 49:10).
Reversal of human fortune: Hannah’s barrenness gave way to children (1 Samuel 1:1–28; 2:21); Samuel became prophet instead of Eli’s sons (2:12; 3:13); Saul rose to prominence though he was from a lowly tribe; and David was anointed king though he was the youngest son (16:1–13). Normal human patterns were reversed by God so that His plan could be furthered, showing His sovereignty over all.
HOW DO I APPLY THIS?
God is still sovereign in the 21st century. He will accomplish His purposes with or without our cooperation. But as was true in the lives of Samuel, Saul, and David, our response to God’s call affects our outcome. Will we obey Him as Samuel and David did and live lives marked by blessing? Or will we, like Saul, try to live on our own terms? “To obey is better than sacrifice,” Samuel told Saul (1 Samuel 15:22). That truth still speaks to us today.
End Notes
1. Norman L. Geisler, A Popular Survey of the Old Testament (Peabody, Mass.: Prince Press, 2007), 107.

